Ceramic Dental Solutions
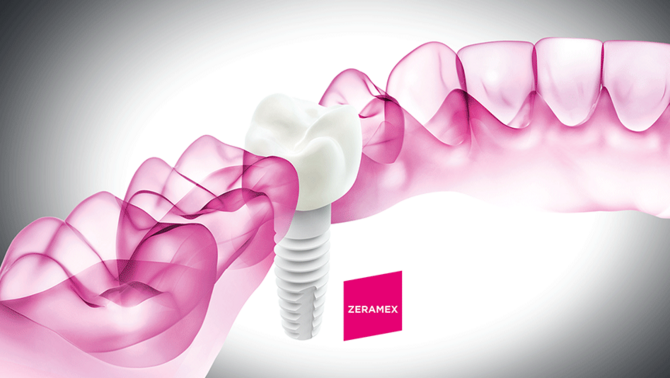
Tooth replacement with biologically sound implant materials continues to grow in popularity. Accordingly, the demand for a suitable alternative to titanium alloys is increasing. Thanks to the excellent biocompatibility and enhanced aesthetic outcome, more and more implantologists and patients show a preference for ceramic implant materials.
As a world innovation leader for advanced ceramics, CeramTec can help you to find the right solution and to achieve the desired level of differentiation. We are drawing on more than 30 years of experience in dental applications and specialist know-how in ceramics.
Over 30 Years of Experience with Dental Ceramics
ISO 13485 certified
Specialized knowledge in development and production of advanced ceramics (ATZ, TZP, ZTA)
Extensive manufacturing know-how including ceramic injection molding
Uncompromising quality management
High volume production capabilities
Partnership and services - supporting you every step of the way

The Biocompatible Choice
For many patients, the choice of a natural material is a high priority in dental implantology. While titanium is a functional choice for dental implants, some patients develop adverse reactions to metals1,2,3 or experience a discoloration of the gums4,5.
Ceramic implants are 100% metal-free. Therefore, dental professionals may find a viable solution with ceramic dental implants1,2 for their patients with metal sensitivity. Ceramics show excellent biocompatibility6,7,8 and are chemically stable in a physiological environment9. They are unlikely to trigger inappropriate immune reactions after implantation.6,7,3
Natural and Aesthetic
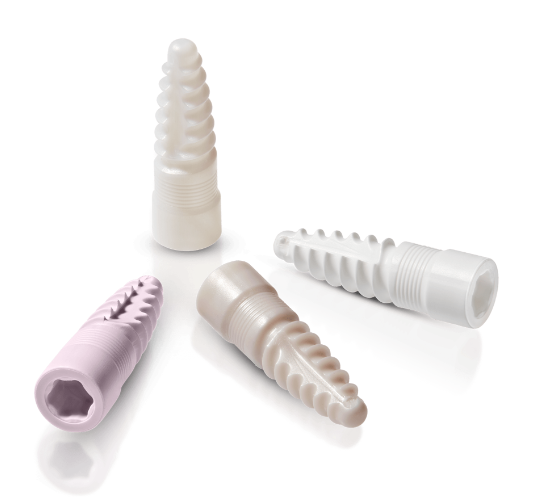
Ceramic materials come in different shades of white mimicking the natural colouring of the tooth. For patients with thin gums, there is no risk of grey colouring shining through (tattooing) as it can occur with metal implants4,5. Ceramic materials do not release metal ions, and therefore do not cause grey stains along the gumline10. The most commonly used materials for dental implants are Zirconia (TZP) and Alumina Toughened Zirconia (ATZ) ceramics.
With ceramic dental implants in your portfolio, you can offer your customers a natural and hypoallergenic choice of dental implants for excellent aesthetic results.

References
*The mentioned claims are based on the long-term experience of ceramic materials/implants in dentistry as described in publicly available literature, mainly focusing on use of zirconia materials (TZP).
**References are available from CeramTec GmbH upon request.
1. Gökçen-Röhlig B, Saruhanoglu A, Cifter ED, Evlioglu G. Applicability of zirconia dental prostheses for metal allergy patients. Int J Prosthodont. 2010;23(6):562-565.
2.Oliva X, Oliva J, Oliva JD. Full-mouth oral rehabilitation in a titanium allergy patient using zirconium oxide dental implants and zirconium oxide restorations. A case report from an ongoing clinical study. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2010;5(2):190-203.
3. Blaschke C, Volz U. Soft and hard tissue response to zirconium dioxide dental implants--a clinical study in man. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006;27 Suppl 1:69-72.
4. Cosgarea R, Gasparik C, Dudea D, Culic B, Dannewitz B, Sculean A. Peri-implant soft tissue colour around titanium and zirconia abutments: a prospective randomized controlled clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(5):537-544. doi:10.1111/clr.12440.
5. de Medeiros RA, Vechiato-Filho AJ, Pellizzer EP, Mazaro JV, dos Santos DM, Goiato MC. Analysis of the peri-implant soft tissues in contact with zirconia abutments: an evidence-based literature review. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013;14(3):567-572. doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1364.
6. Kajiwara N, Masaki C, Mukaibo T, Kondo Y, Nakamoto T, Hosokawa R. Soft tissue biological response to zirconia and metal implant abutments compared with natural tooth: microcirculation monitoring as a novel bioindicator. Implant Dent. 2015; 24(1):37-41. doi:10.1097/ID.0000000000000167.
7. Bächle M, Butz F, Hübner U, Bakalinis E, Kohal RJ. Behavior of CAL72 osteoblast-like cells cultured on zirconia ceramics with different surface topographies. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18(1):53-59. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01292.x.
8. Cionca N, Hashim D, Mombelli A. Zirconia dental implants: where are we now, and where are we heading? Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):241-258. doi:10.1111/prd.12180.
9. Siddiqui DA, Guida L, Sridhar S, Valderrama P, Wilson TG Jr, Rodrigues DC. Evaluation of oral microbial corrosion on the surface degradation of dental implant materials. J Periodontol. 2019;90(1):72-81. doi:10.1002/JPER.18-0110.
10. Noumbissi S, Scarano A, Gupta S. A Literature review study on atomic ions dissolution of titanium and its alloys in implant dentistry. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(3):368. doi:10.3390/ma12030368.
11. Scarano A, Piattelli M, Caputi S, Favero GA, Piattelli A. Bacterial adhesion on commercially pure titanium and zirconium oxide disks: an in vivo human study. J Periodontol. 2004;75(2):292-296. doi:10.1902/jop.2004.75.2.292.
12. Rimondini L, Cerroni L, Carrassi A, Torricelli P. Bacterial colonization of zirconia ceramic surfaces: an in vitro and in vivo study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17(6):793-798.
13. Roehling S, Astasov-Frauenhoffer M, Hauser-Gerspach I, et al. In vitro biofilm formation on titanium and zirconia implant surfaces. J Periodontol. 2017;88(3):298-307. doi:10.1902/jop.2016.160245.